~ Issac Newton
Human Monoclonal Antibody Blocking SARS-CoV-2 Infection:
A lot of research work and articles on treatment techniques, vaccine development and drug discovery has been on the global news off late since the outbreak of the novel Coronavirus. Some of them are pretty famous now, namely, Plasma Technology, Stem Cell Therapy, usage of drugs like Hydroxylcholoroquine, RNA Vaccine, etc. All of them are extremely great research outputs which are experimented and significantly developed in a short span of time. Yet out of all of these, the one, most recent method of treatment that I felt is striking and has the potential to render promising results is Human Monoclonal Antibodies produced from Hybridoma Technology, used to cure and detect the SARS-CoV-2. This article primarily aims to sum up this antibody producing technology based on the recent findings to cure SARS-CoV2 infection in a much simpler way.
Let's dive into the basics of biology related to research work to comprehend better.
BASICS OF IMMUNE SYSTEM:
The immune system in humans gets activated when an Antigen (denoted as Ag), a molecule or molecular structure of a foreign body triggers an immune response to release an Antibody (denoted as Ab), Y-shaped protein produced mainly by plasma cells that is used by the immune system to neutralize pathogens such as bacteria and viruses. Antibodies are also called as Immunoglobulins (denoted as Ig) and are of different types. The immunoglobulin that is used in the production of human monoclonal antibody against SARS-CoV2 is IgG1 (the below figure shows the basic structure of IgG). Therefore we understand that antibodies are produced as an immune response by one of cells of the immune system, B-Lymphocytes, when an antigen enters the body. This process naturally occurs in our immune system.
Then why are we researching the same which is inherently present in our system? Why are the antibodies tagged as 'Monoclonal'? The answer is simple. Due to endocytic self - replication of the virus and extreme pathogenesis, the immune system is bluffed and backfired. The rate of viral replication within a single cell is high and therefore is leading to lethality/ prolonged cure/ reversions in the patients. When the immune system is bluffed and is loaded with high virion content or severe inflammation, the body loses the immunity or the innate immunity of the patient doesn't suffice to battle against the virus. Therefore a vaccine or a drug is administered externally either to boost the immune system or to neutralize the coronavirus.
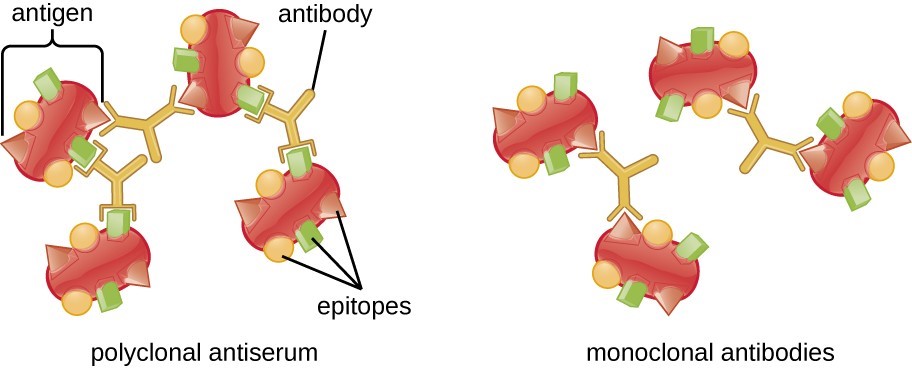
The monoclonal antibodies have the potential to do both. The usage of such antibodies makes it unique because they are monoclonal by nature, meaning these antibodies bind specifically to an epitope (the antibody binding site present on antigen) on an antigen. Polyclonal Antibodies present in serum, naturally available in the human body, are a heterogeneous population released by a different population of B-Lymphocytes. The polyclonal antibodies are not usually antigen specific and it takes a prolonged period for the body to adjust itself to produce antibodies that can potentially fight against the virus. The monoclonal antibodies (mAb) have an edge over the polyclonal because they are site-specific, highly reactive in a lesser time span.
 |
| Epitopes: Antigen-Binding Sites (Source: Lumen Learning) |
 |
| (Source: Creative-diagnostics.com) |
HYBRIDOMA TECHNOLOGY FOR MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY PRODUCTION:
The monoclonal antibody production is done only by animal cell lines. Cell Lines are defined as a population of cells descended from a single cell and contain the same genetic make up. The cell lines are of two types - Finite Cell Lines, having limited life span and Infinite Cell Lines, which are immortal.
Monoclonal Antibodies are produced by antigen-activated B-Lymphocytes that have been immortalized by hybridizing them with immortal cell lines (eg. cancer cells). This technique of cell fusion to produce a new recombinant cell with mixed traits is called Hybridoma Technology. It fuses antibodies producing B-lymphocytes with immortal cell lines using Polyethylene Glycol (PEG). The so produced hybrid cell is screened in the HAT nutrient medium and then recovered. The recovered cells from the medium are artificially scaled up to larger quantities by Cloning, the process of producing genetically identical individuals of an organism either naturally or artificially. From the large quantity of hybrid cells - monoclonal in nature, that is produced by single lineage of cell - the monoclonal antibodies are harvested.
This is the basic procedure of cell hybridization to produce recombinant cells. To develop the human monoclonal antibody against the SARS-CoV2 different cell lines were used for hybridizing but primarily this technique was followed.
 |
| Hybridoma Technology for Monoclonal Antibody Production (Source: Research Gate) |
ELISA:
The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay is a commonly used analytical biochemistry assay, first described by Engvall and Perlmann in 1971. The assay uses a solid-phase enzyme immunoassay to detect the presence of an antigen in a liquid sample using antibodies directed against the protein to be measured. The type of assay used in the experiment of SARS-Cov2 is ELISA (cross) Reactivity. Cross-reactivity occurs when an antibody raised against one specific antigen recognizes two antigens that have similar structural regions.
 |
| ELISA Technique (Source: AAT Bioquest) |
PROTEIN STRUCTURE:
Protein structure is the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in an amino acid-chain molecule. Proteins are polymers – specifically polypeptides – formed from sequences of amino acids. The structure of the protein correlates to the function of protein. Any conformational changes in the protein structure leads to change or deactivation of protein function. Huge proteins are made of protein subunits made of a cluster of amino acid chains. A protein subunit is a single protein molecule that assembles with other protein molecules to form a protein complex. For example, the hemoglobin protein is made of four subunits which are connected by Iron molecules.
 |
| Hemoglobin Protein Structure (Source: Think Health) |
Human Monoclonal Antibody Blocking SARS-CoV-2 Infection:
The novel Coronavirus has seen an outbreak in the past in the year 2002. The previous outbreak was an epidemic and affected nearly 8000 cases with 10% of lethality. The human monoclonal antibodies are developed from a comparative study between wild type, SARS-CoV (prevalent in 2002) and mutated type, SARS-Cov-2 (currently prevalent)in a cell culture. This cross-neutralizing antibody targets a communal epitope on these viruses and may offer potential for prevention and treatment of COVID-19.
NOTE:- Neutralizing refers to the process in which the antibody neutralizes the effect of a pathogen (antigen) by acting on the specific receptors. Cross-neutralization refers to the process where a single antibody is capable of neutralizing different types of antigens.
Monoclonal Antibodies targeting vulnerable sites on the viral surface can be used as a drug. The CoV-neutralizing antibody primarily targets trimeric Spike (S) glycoprotein, present on the surface of the virus that mediates its entry into the host cell. To know more about the structure and viral replication, please refer to An Insight on SARS-CoV-2. The spike protein has two functional subunits - S1 unit with four core domains (S1A, S1B, S1C, S1D) mediates cell attachment and S2 unit functions for the fusion of viral and host cellular membrane. Neutralizing antibodies often target receptor sites in S1 subunit to disable receptor interactions. ACE-2 is an enzyme-like protein, present on epithelial cells, is the host receptor. Fusion of membrane occurs when the ACE-2 receptor binds with the Spike protein through the S1B domain of the virus. This receptor interaction triggers irreversible conformational changes that enable Spike protein fusion with the membrane. The evidence for binding of ACE-2 receptor and monoclonal antibody with the S1B receptor domain is validated through ELISA tests.
| (Source: REUTERS/Thomas Peter) |
ELISA cross reactivity was done on antibody containing supernatant of a collection of 51 SARS-(S) hybridoma cells derived from immunized transgenic mice that encode chimeric (recombinant) Immunoglobulin with human variable heavy and light chains and constant regions of rat origin. The so produced monoclonal antibody (mAb) codes as 47D11 and is reformatted into a fully human IgG1 isotype. The recombinant human 47D11 monoclonal IgG1 antibody was used as a final monoclonal antibody product. The human 47D11 mAb through ELISA showed that it is binding to the S1B receptor binding domain of Spike protein, subsequently neutralizing the antigen/spike protein. A remarkable observation was that the 47D11 IgG1 monoclonal antibody binding to S1B domain did not compete with S1B binding to ACE-2 receptor on the cell surface, as shown by flow cytometry. Therefore there would not be a competition between ACE-2 and 47D11 IgG1 mAb which further helps the monoclonal antibody to predominantly bind to the S1B domain of spike protein in order to neutralize the antigen/antigen protein. Using a trypsin triggered cell-cell fusion assay accounted that 47D11 IgG1 mAb was shown to impair SARS-(S)-mediated syncytia formation. It is ultimately assumed that mAb is blocking the entry of the virus into the host cells and renders a greater scope of neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 outside the cell. But it is noted that 47D11 mAb neutralizes Coronavirus through a yet unknown mechanism that is different from receptor binding domain inhibition.
CONCLUSION
The monoclonal antibodies are a significant breakthrough for the treatment of SARS-CoV-2. The production of monoclonal antibodies is done by the usage of Recombinant DNA technology, Hybridoma Technology and cell culture techniques. The screening methods followed are ELISA and SDS-PAGE. The 47D11 monoclonal antibody binds to the S1 subunit receptor binding domain of Spike protein and further neutralizes its (Spike Protein) activity. It is self-explanatory that ACE-2 host receptor loses it's scope of binding with S1 subunit when there is administration of high concentration of monoclonal antibodies to the patient. It significantly reduced the viral attack and hence is pivotal in the treatment.
Comments
Post a Comment